Diode
The diode is one of the oldest and most important electronic devices, although it is not as famous as its cousin, the transistor. Used in all sorts of electrical and electronic systems, the diode functions as a one-way valve for electric current—it only allows current to flow in one direction. This is useful in converting AC to DC, processing high frequency signals, regulating voltages, and in other applications. There are two basic types of diodes. One is an electron tube similar to the triode. The other type uses semiconductors, like the transistor. Both were invented early in the 20th century.
The first diode was a modified light bulb. Thomas Edison discovered that including an extra electrode in a light bulb and connecting it to the positive side of a battery resulted in a current flowing from the filament through the empty space. He was not sure what to do with this discovery, and moved on to other projects.
Joseph J. Thomson (1856~1940) announced the discovery of the electron in April 1897 and explained the Edison effect where current travels just one way through a vacuum tube. Thompson received a Nobel prize in 1906.
Others found another use for this device. In the early 1900s, for example, English engineer John Ambrose Fleming used this one-way electrical “valve,” to convert radio waves into a flow of current that could be measured by a galvanometer. The Fleming valve is remembered as the first true electronic device. It came into use for radio transmission and soon became the basis of Lee De Forest’s Audion electron tube, which he invented in 1906.
Also around 1906, American engineer Greenleaf W. Pickard invented a new type of diode. Pickard based his design on the earlier discovery that electricity can flow in only one direction through certain types of mineral crystals, such as silicon. By placing a silicon crystal between a metal base and a carefully placed fine wire, Pickard created a valve that could also be used to detect radio waves. This type of “cat’s whisker” diode (so-named because of the fine wire used in it) became more popular after American H. C. Dunwoody patented a version of it that used a material called carborundum.

In the early 1900s, cat’s whisker diodes were widely used in radio receivers, as they were an improvement over electron tubes. But they too had limitations. They required careful adjustment and could easily be knocked out of alignment. For these reasons the use of cat’s whisker diodes declined, although their ability to work at very high frequencies made them valuable during World War II when they were used in radar receivers. During the war years, thousands were manufactured, and in the course of research on semiconductors, Bell Laboratories scientists stumbled on a new type of diode. Russell Ohl, a Bell Labs metallurgist working with silicon samples discovered that one of his samples acted like a diode and—even more remarkable—produced electricity in response to light. He had invented a new type of diode that was also an efficient solar energy converter or “cell.” The reason it worked either as a diode or as a solar cell was a mystery to the researchers. Eventually, however, they determined that the sample, which had been cut from a larger piece of silicon, had a region that contained high levels of a certain kind of impurity. The area where this region joined the rest of the silicon formed a “junction.” This junction had something to do with the diode action of the device. The junction and the different regions of impurity also allowed it to respond to light. It would be many years before physicists explained why this worked, but in the meantime, semiconductor junction diodes went into production, first as solar cells and eventually as ordinary diodes.
Today the variety of diodes and their uses have greatly expanded. Electron-tube diodes are rarely used, but silicon diodes are used in many types of equipment to detect high frequency electromagnetic waves, to convert sunlight into electricity, and many other purposes. Inside computers, televisions, and other familiar systems are diodes that help convert alternating current (AC) electricity to direct current (DC), and to regulate the level of the voltage. High-power diodes are used in automobiles, where they convert the AC from the alternator into DC that the battery and on-board electronics can use. Light emitting diodes (LEDs), perfected in the early 1960s, have replaced incandescent lamps for many purposes, and may soon replace the lamps used in car headlights and household light bulbs.
Historical Diodes (Rectifiers)
Here is a partial list of the type of diodes invented, constructed and used over time, many comprise of hazardous materials:
- Chemical Rectifier, known as the Nodon Valve using lead and aluminium electrodes.
- Copper type rectifier (used lead and copper junctions, also copper sulphide and magnesium junctions)
- Selenium Rectifier
- Electrolytic Rectifier
- Gaseous Rectifier, Argon arc rectifier
- Mechanical Rectifier, colloquially known as the vibrator, obsoleted from industrial applications around 1921, but used in vacuum tube mobile radio equipment up until 1958. Also a rotational synchronous rectifier
- Mercury Arc Rectifier, also Mercury Vapour Rectifier
- Photo diode tube, also photomultiplier, gamma ray detector
More recent solid state diodes:
- Silicon Diode,
- Germanium Diode,
- Tunnel Diode,
- IMPATT Diode,
- Gunn Diode,
- Schottky Diode,
- Varacter Diode,
- Zener Diode,
- Light Emitting Diode,
- Photodiode,
- Silicon Controlled rectifier (SCR)
- Metal-Oxide-Metal Diode, invented around 1975, and a variant of the Schotty diode, see text authors V A Ivanov, A A Rivlin and V S Solov'ev and Izmeritelnaya Tekhnika, No. 11, p. 33, November, 1980. Used for detection and mixers into the near-infra-red wavelengths.
S Tube Rectifier
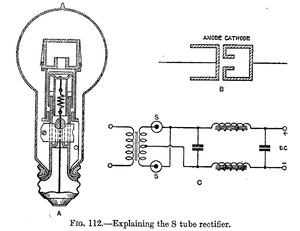
The S Tube Rectifier.-The S tube rectifier has been developed by the American Radio and Research Corporation, and is often used by American amateurs instead of the usual form of two-electrode valve rectifier. The anode is a flat carbon electrode, and the cathode is cup-shaped, with a small tube-like opening, as illustrated. The tube contains helium at about 12 mm. pressure. When the anode is made positive, free electrons are drawn from all parts of the cup through the opening to the anode.
In doing so they collide with the atoms of the helium and ionise them. The action is cumulative, and hence the tube conducts.
When the cup is made positive the action is very different. Positive ions in the cup, being much larger in bulk, are less mobile, and but comparatively few of them reach the cathode (cup). The movement of the positive ions is so sluggish, and the number which reach the cathode so few, that the current conduction is less than 1 per cent. of the normal current carrying capacity when the polarity is reversed.
S tubes are manufactured for supplying D.C. anode potentials to 5-watt 1 transmitting valves. They are rated at 20 watts each, the normal current being 50 milliamperes. The tube has a practically constant drop of 150 volts, and will stand 2,000 volts in the reverse direction. Two rectifier tubes will supply sufficient current for one 50-watt 1 transmitting valve.
Other old diodes were:
- Raytheon Rectifiers
- Tantalum rectifier uses tantalum and lead electrodes, with sulphuric acid. Similar to the Nodon valve.
- Vacuum tube diode
- Cats Whisker, uses crystalline galena (Lead sulphide), it can also use coal.
- Crystalline Zinc Diode, exhibits negative resistance akin to the modern day tunnel diode. see -> http://www.sparkbangbuzz.com/els/znrfamp2-el.htm